Roberta SPEAKER – Easily design your own dialog assistant
Develop your own dialog assistant in an intuitive way – with the visual, no-code programming interface »Open Roberta®«!
In which areas does the AI application offer the greatest benefit?
Speech technologies play a key role in the development of new digital services and technologies and already serve as a reliable assistant at home. Whether Alexa or Siri, voice communication with computers has long since arrived in everyday life: A quick question about the likelihood of rain or the risk of traffic jams on the way home, as well as controlling music or lights within your own four walls – communication with voice assistants is becoming increasingly common. But how can voice assistants be used in companies or even in schools?
Data-secure, customized – Roberta SPEAKER for companies and in education
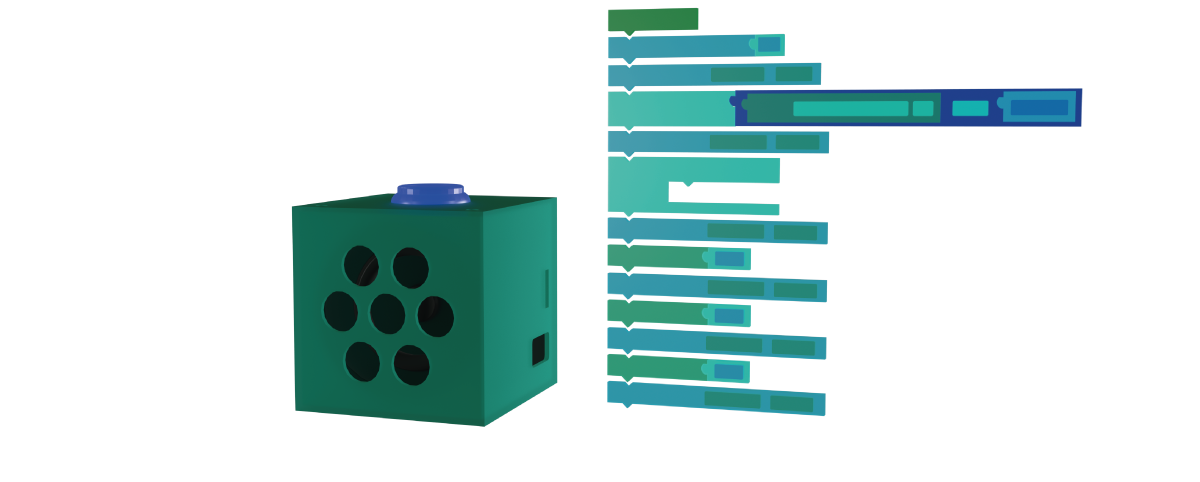
The KI.NRW demonstrator »Roberta SPEAKER« allows even programming novices to develop dialog functions easily and intuitively on their own. Users from different industries can benefit from this: The technology enables companies to develop their own dialog assistants, for instance to control their machines via voice commands. In addition to the autonomous design of the dialogs, the advantages also include data security, because unlike many commercial voice assistants, Roberta SPEAKER does not require an internet connection – all data is processed locally. Teachers and educational stakeholders will also be able to use Roberta SPEAKER in the future to better teach young people about the use of AI technologies in everyday life and build their digital skills.
The programming language for dialog control is NEPO®, which is assembled on the open-source platform Open Roberta from Fraunhofer IAIS using »drag and drop«, thus avoiding obstacles such as typing or syntax errors. The speech recognition model can be adapted specifically to the user’s own requirements and thus run on a microcomputer. As a result, there is no need for expensive and complex hardware. For the communication between users and voice assistants, additional elements such as a microphone and speakers are also included.
The demonstrator was developed as part of the SPEAKER project funded by the German Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Climate Action (BMWK). The SPEAKER project aims to establish a leading voice assistance platform »made in Germany« for business-to-business (B2B) applications. The platform is intended to be open, modular, and scalable and provide technologies, services, and data via service interfaces. The consortium leaders are the Fraunhofer Institutes IAIS and IIS.
What are Roberta SPEAKER’s quality characteristics?
- Low effort: The KI.NRW demonstrator shows that AI language models can work even on a small (portable) processor. This opens up innovative functional possibilities. One of the benefits is that the AI models work locally, so there is no need for an internet connection. This way, the Roberta SPEAKER box demonstrates that voice assistants can be implemented almost anywhere to interact with people and carry out simple tasks with little effort.
- Intuitive and individually customizable: The intuitive programming interface allows everyone to easily develop functioning program sequences, so that students can generate their own voice commands using the demonstrator. The programming interface is the Open Roberta Lab, a freely available, data-secure, and open programming platform developed by the educational initiative »Roberta® – Learning with Robots« by Fraunhofer IAIS.
- Easy communication: By using artificial intelligence, users can communicate with the voice assistants via spoken language. The dialog assistant understands questions and commands, can derive actions from the user’s intentions and can formulate answers and communicate these via the loudspeaker or derive actions.
- Powerful and resource-saving: The voice-controlled box is only ready for use when the artificial intelligence technologies, the AI models, can function on a small processor. This is why the developers are focusing on resource-saving AI technology.
»Dialog systems are everywhere. With ›Roberta Speaker‹, we make it possible for anyone to create their own dialogs to control IoT devices using drag-and-drop with almost no prior knowledge.«
Which AI technology is used in the KI.NRW demonstrator?
Technical systems capable of understanding spoken commands allow for natural communication between humans and machines. Speech recognition reliably converts spoken information into digital text in real time – even under difficult conditions, such as when there is background noise, as can occur in an industrial environment, for example, or when regional dialects are spoken.
Only domain-specific knowledge makes the language system useful in certain areas of application. Intent recognition, the recognition of intentions from the spoken text, plays a key role here. An intent classifier recognizes the subject of the text and searches for the factual answer. With the help of verbalization techniques, the system then ensures that the response is fully formulated.
In human-machine interaction, it is often an advantage when text information does not have to be read, from a display for instance, but is transmitted using natural speech. Based on deep learning technology, state-of-the-art algorithms generate highly natural-sounding speech output with excellent intelligibility and fluent intonation.
What does the AI demonstrator show?
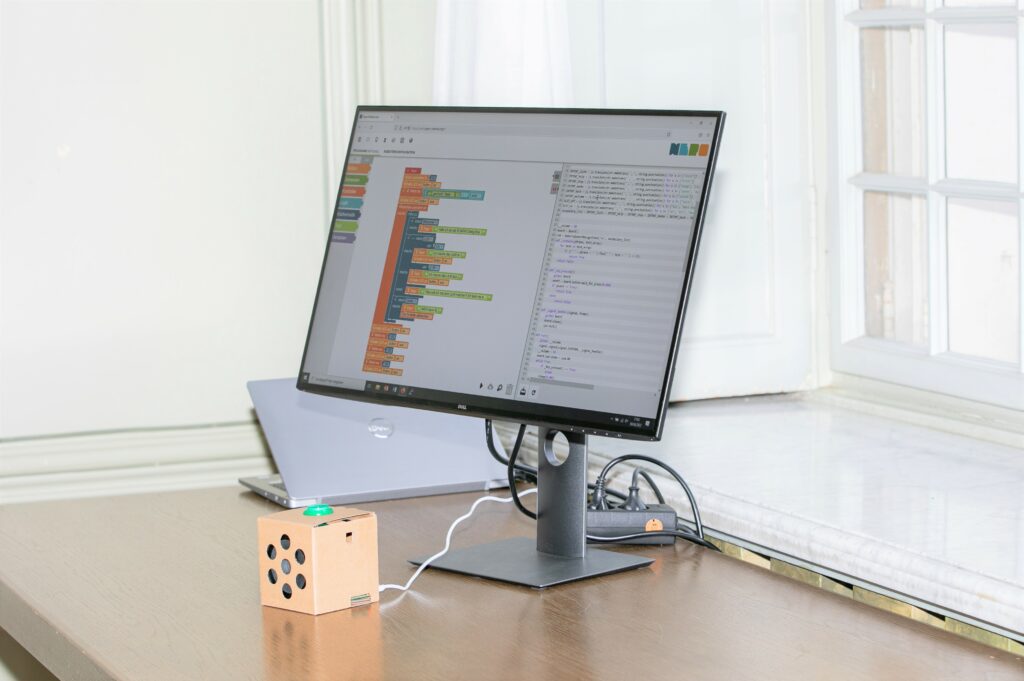

The KI.NRW demonstrator »Roberta SPEAKER« allows both companies and students from different types of schools, such as secondary schools or vocational schools, to develop their own voice assistant using a simple programming interface. In this way, the expression »do it yourself« is given a new meaning and people can start learning about AI technologies without any prior knowledge.
Request a non-binding consultation with our experts now!
Where can I find more information?
Study »Modern language technologies«
Find out where we encounter modern language technologies in everyday life and at work and what economic opportunities they offer.
Roberta SPEAKER for companies
Are you interested in using Roberta SPEAKER to conduct AI trainings in your company or would you like to know how you can integrate the Fraunhofer language technology into your processes?
Roberta SPEAKER in education
Do you want to use Roberta SPEAKER in an educational context?
Contact the team of developers

Thorsten Leimbach
Head of Smart Coding and Learning
Fraunhofer IAIS
Schloss Birlinghoven
53757 Sankt Augustin
Phone +49 2241 142404

Beate Jost
Technical Manager at Roberta
Fraunhofer IAIS
Schloss Birlinghoven
53757 Sankt Augustin
Phone +49 2241 142441

Dr.-Ing. Oliver Walter
Team leader
Real Time Speech Recognition
Fraunhofer IAIS
Schloss Birlinghoven
53757 Sankt Augustin
Phone +49 2241 2541